Vendor description
"We are a technology company focused on industry, infrastructure, transport, and healthcare. From more resource-efficient factories, resilient supply chains, and smarter buildings and grids, to cleaner and more comfortable transportation as well as advanced healthcare, we create technology with purpose adding real value for customers."
Source: https://new.siemens.com/global/en/company/about.html
Business recommendation
Upgrade to the latest firmware version to mitigate the buffer overflow.
The hardware (SM-2558) is considered end of life (EOL), thus no new version with a fixed JTAG will be released. Restrict physical access to the device.
SEC Consult highly recommends to perform a thorough security review of the product conducted by security professionals to identify and resolve potential further security issues.
Vulnerability overview/description
1) Unlocked JTAG Interface of Zynq-7000 on SM-2558
The JTAG interface can be accessed with physical access to the PCB. After slightly modifying the hardware it is possible to connect to the interface with full access to the communication module.
2) Buffer Overflow on the Webserver of the SM-2558, CP-2016 & CP-2019 (CVE-2024-31484)
The webserver running on the SM-2558 device as well as CP-2016 and CP-2019 is vulnerable to a buffer overflow vulnerability.
The value of the HTTP header "Session-ID" is processed and used in an "sprintf" call without proper length checking. The target buffer is in the BSS segment and likely 1024 bytes in length. The buffer overflows into several other global data structures.
Proof of concept
1) Unlocked JTAG Interface of Zynq-7000 on SM-2558
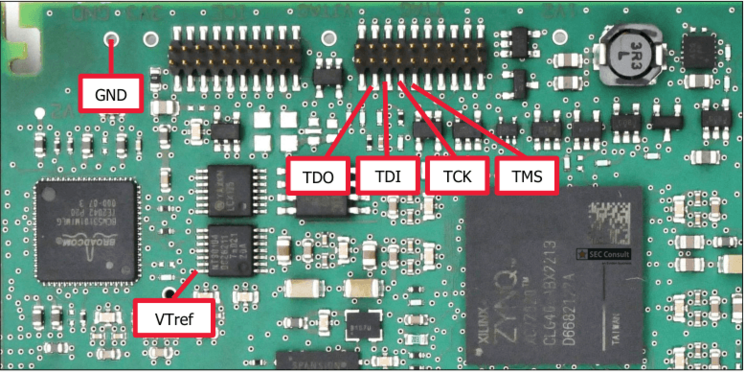
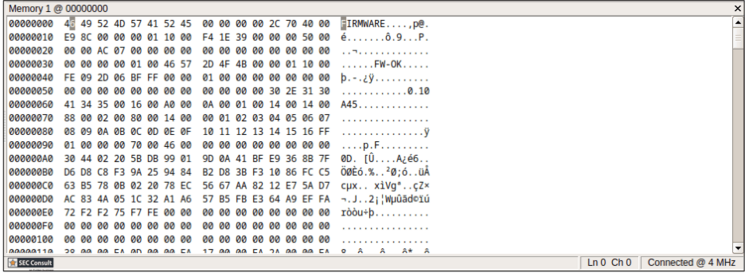
The JTAG interface pins (TDI, TDO, TCK, TMS, GND) are accessible on a populated 20-pin header on the PCB (see figure_1).
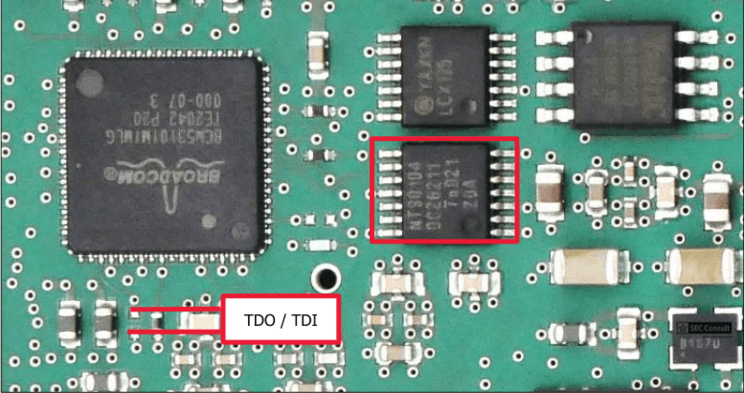
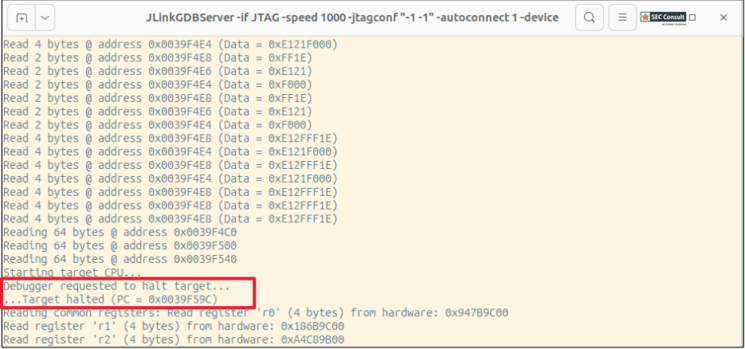
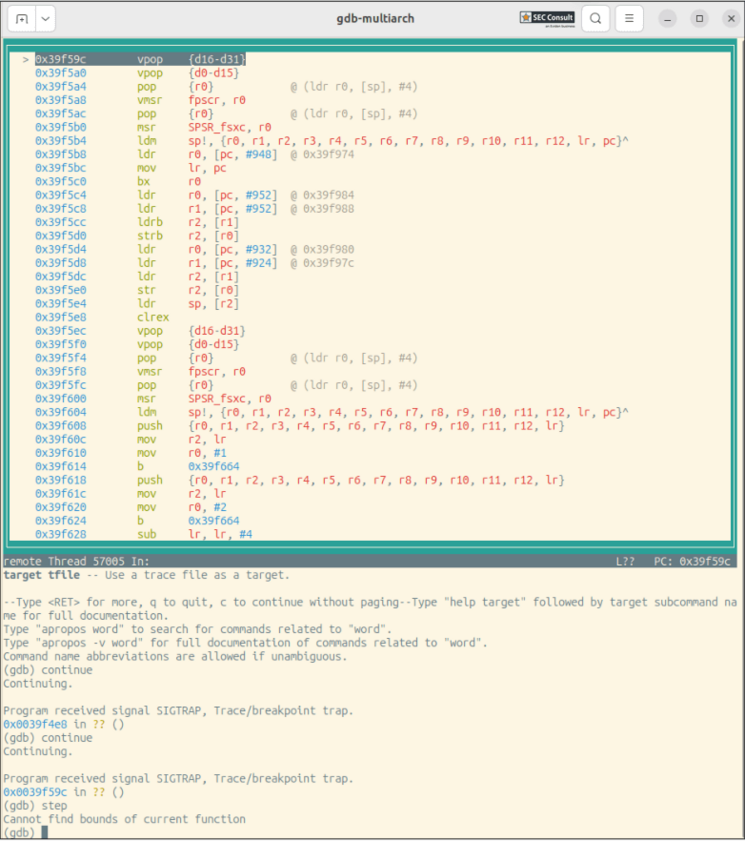
A removed connection needs to be restored by soldering an additional wire between two exposed contacts (see figure_2), as the JTAG interface of the Zynq-7000 is daisy-chained with the JTAG interface of the Broadcom BCM53101M Ethernet controller. The pad in question connects to pin A57 (TDI) of the Ethernet controller. After connecting to the pins, a connection to the Zynq-7000 JTAG interface is possible. E.g., memory can be dumped (figure 5), execution can be single stepped (figure 4) or halted (figure 3), and variables changed. This grants an attacker with physical access full control of the communication module.