Technical details about the research results are presented during the annual Troopers Security Conference 2023 titled "Everyone knows SAP, everyone uses SAP, everyone uses RFC, no one knows RFC: From RFC to RCE 16 years later" in Heidelberg, Germany.
Responsible Disclosure of an Exploit Chain Targeting the RFC Interface Implementation in SAP® Application Server for ABAP
vulnerability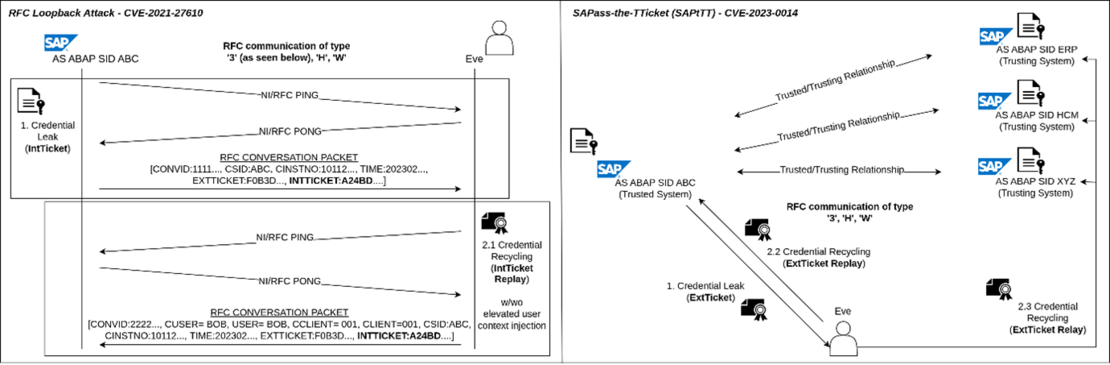
Overview of Attacks and Vulnerabilities
Whitepaper
Findings of the Study: Overview of Attacks and Vulnerabilities
CVE-2021-27610: Design Flaws and Weaknesses in System-Internal Communication Architecture
In SAP software systems based on the ABAP technology stack, an implicit trust architecture for system-internal RFC and HTTP communication scenarios exists. This architecture was found to implement an insecure and weak design that can be exploited remotely to bypass authentication and/or escalate privileges, aka “RFC Loopback Attack”.
Adversaries receiving an ordinary request from a vulnerable system can craft their own communication with the system in a reflection attack where they reuse leaked logon material to claim a trusted identity and impersonate user accounts. Other attack vectors include sniffing of unencrypted network traffic and post-exploitation actions. Successful exploitation can result in full system compromise.
The vendor issued a patch with SAP Security Note 3007182, which has been released in the course of Patch Tuesday June 2021. Please refer to 3007182 for affected versions and correction instructions.
CVE-2023-0014: Design Flaws and Weaknesses in the Trusted/Trusting Architecture
In SAP software systems based on the ABAP technology stack, an explicit trust architecture for cross-system RFC and HTTP communication scenarios, known as trusted/trusting relationships, exists. This architecture was found to implement an insecure and weak design that can be exploited remotely to gain illegitimate access to vulnerable systems and move laterally in SAP system landscapes, aka “SAPass-the-TTicket (SAPtTT)”.
Adversaries receiving an ordinary request from a vulnerable system can craft their own communication with the same system, or with other systems being in a trust relationship with the vulnerable system, in reflection and deflection attacks where they reuse leaked logon material to claim a trusted identity and impersonate user accounts. Other attack vectors include sniffing of unencrypted network traffic and post-exploitation actions such as signature forgery. Successful exploitation can result in full system compromise.
The vendor issued a patch with SAP Security Note 3089413, which has been released in the course of Patch Tuesday January 2023. Please refer to 3089413 for affected versions and correction instructions.
CVE-2021-33677: Information Disclosure in AutoABAP/bgRFC Interface
Dialog instances of the AS ABAP provide the RFC Gateway service on a port between TCP/3300- 3399. This service was found to expose specific functions to authenticated yet unauthorized users. Within these functions, several vulnerabilities have been identified that can be exploited remotely to enumerate valid user accounts and get the server to perform requests to chosen hosts and ports in range TCP/3300-3399. The latter can be exploited with limited server-side request forgery primitives that trigger an RFC function call of a predefined function module.
Adversaries may combine these primitives with CVE-2021-27610 and CVE-2023-0014 to exfiltrate and deploy reusable logon material in further attacks.
The vendor issued a patch with SAP Security Note 3044754, which has been released in the course of Patch Tuesday July 2021. Please refer to 3044754 for affected versions and correction instructions.
CVE-2021-33684: Out-of-Bounds Write in Scrambling Routine disp+work!ab_scramble
Dialog instances of the AS ABAP provide the RFC Gateway service on a port between TCP/3300- 3399. This service was found to expose the system to a memory corruption bug triggered when kernel binary disp+work parses specially crafted RFC packets that include malformed logon material. The vulnerability can be exploited remotely to crash disp+work processes, corrupt the integrity of data used during authentication, or potentially gain code execution. The latter was not verified.
On vulnerable 64-bit versions of disp+work, available write primitives were successfully tested for an authentication bypass in which the virtual user context of the hard-coded SAPSYS account that possesses no authorizations is hijacked. Remote unauthenticated adversaries may take advantage of this user context to trigger CVE-2021-33677.
The vendor issued a patch with SAP Security Note 3032624, which has been released in the course of Patch Tuesday July 2021. Please refer to 3032624 for affected versions and correction instructions.
In a laboratory environment, a functional exploit that chains multiple primitives of the aforementioned issues for pre-authentication Remote Code Execution has been developed and successfully tested on vulnerable AS ABAP instances running on 64-bit versions of ABAP kernel releases 753 and 777.
Mitigation and Countermeasures
SAP users are advised to upgrade affected software components and implement all necessary post-installation steps to secure systems against the attack vectors found. It is recommended to read the provided Security Notes carefully and adhere to the correction instructions given, if not already done.
With regard to Security Note 3089413, it must be ensured that all prerequisites are met before implementing the corrections, as described in SAP Note 3224161. For all systems in question, it must be ensured that all trusted/trusting relationships are migrated to security method 3 successfully. Finally, it must be ensured that all application servers enforce the newest security method by setting profile parameter rfc/allowoldticket4tt = ‘no’ in the default profile (DEFAULT.PFL) after migration of all connections in the SAP system landscape. The following references contain additional helpful information for applying the patches:
- SAP Note 3224161 - Prerequisites for Note 3089413
- SAP Note 3281854 - FAQ for Security Note 3089413
- SAP Note 3157268 - How-To-Guide: Migration of Trusted/Trusting Relationships
- SAP Support Wiki: Security Notes Webinar 2023-01 – Note 3089413 - Capture-replay vulnerability in SAP NetWeaver AS for ABAP and ABAP Platform
- SAP Support Wiki: Security Notes Webinar 2023-02 – Note 3089413 - Capture-replay vulnerability in SAP NetWeaver AS for ABAP and ABAP Platform (reloaded)
We are not aware of any fully functional workaround that would mitigate all of the issues discovered and would be practical applicable in a short-term view ("quick win"). In case patching is not an option, we highly advise to limit network-wise access (RFC/HTTP) to vulnerable servers as far as possible in order to minimize the available attack surface. Furthermore, we advise to fully enforce encrypted server-to-server communications by means of HTTPS and SNC, reduce S_RFC and S_RFCACL authorization distributions to an absolute minimum, restrict and monitor function calls of function module RFC_TRUSTED_SYSTEM_SECURITY, and limit RFCSYSACL table access. Lastly, we refer to the additional measures described by the vendor in the corresponding SAP notes and in the FAQ for Security Note 3089413.
We are aware that patching customized SAP software systems requires reasonable efforts. Since patches and correction instructions have been available for a considerable amount of time, we close the responsible disclosure process with the coordinated release of technical details further discussed in the published whitepaper.
This research was done by Fabian Hagg and published on behalf of the SEC Consult Vulnerability Lab.