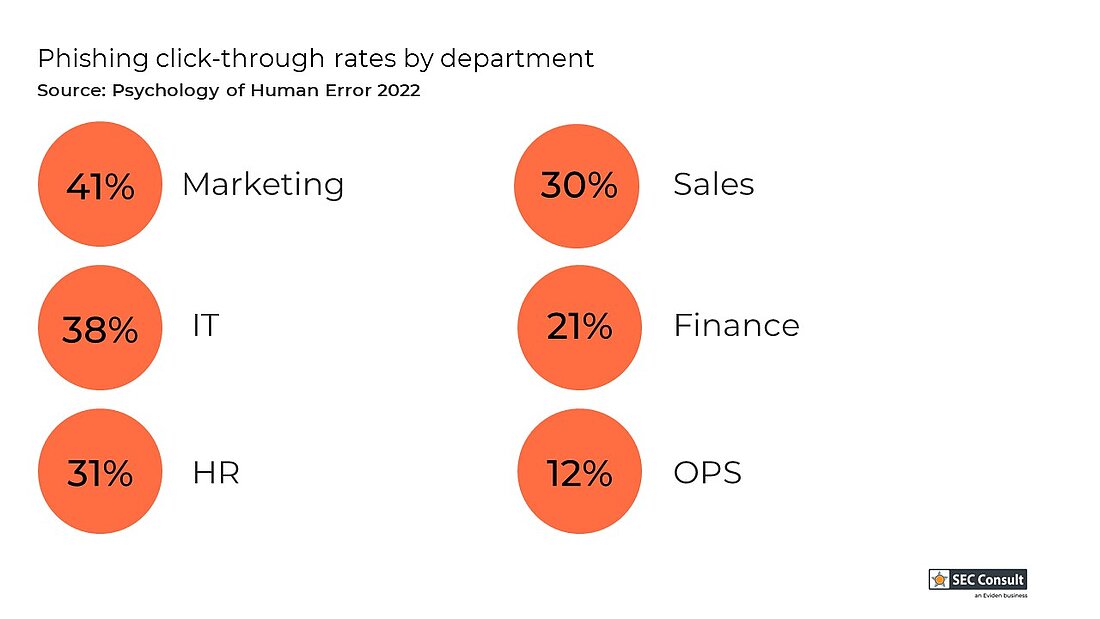
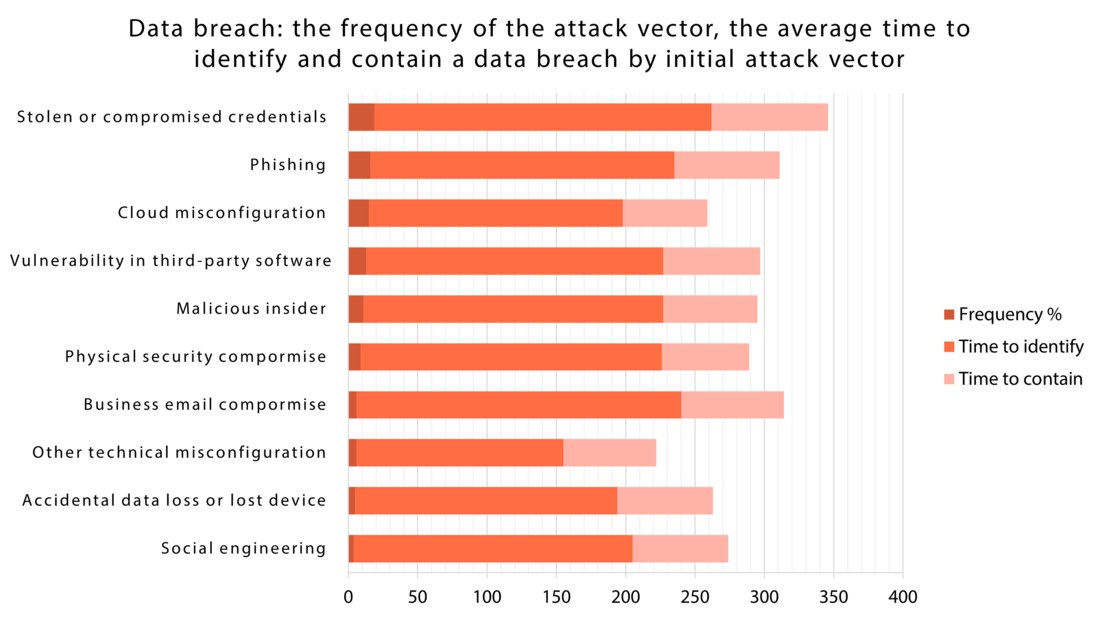
Human factor is considered as one of the top-10 concerns in cyberspace in 2023. It is as prominent cause of concern than external attacks. Researchers have found that approximately 88 % of all data breaches are caused by an employee mistake. So, cybersecurity is not simply a technological issue.
What does human factor mean in the context of cybersecurity?
- The human factor in cybersecurity refers to situations where human error results in a successful data or security breach.
- Human error is defined as a user error, falling for a phishing attack or a malicious insider action.
- It can be a result from negligence, a lack of awareness or inappropriate access controls.
Humans are considered as the weakest component in the security of any IT infrastructure and imply the greatest risks and threats to an organization.
The causes of incidents in the context of human factor
The incidents are caused both from employees with little knowledge in cybersecurity, but also from IT professionals. In the literature the human factor is divided into three large categories: